What would the world be like if we had only black, and African superheroes?
Hard to imagine right?

As difficult as it is to imagine a world filled with African superheroes, it is just as challenging to picture our primary healthcare centers in Nigeria fully integrated with technology, especially considering the persistent issues of poor infrastructure, inadequate funding, and systemic neglect.
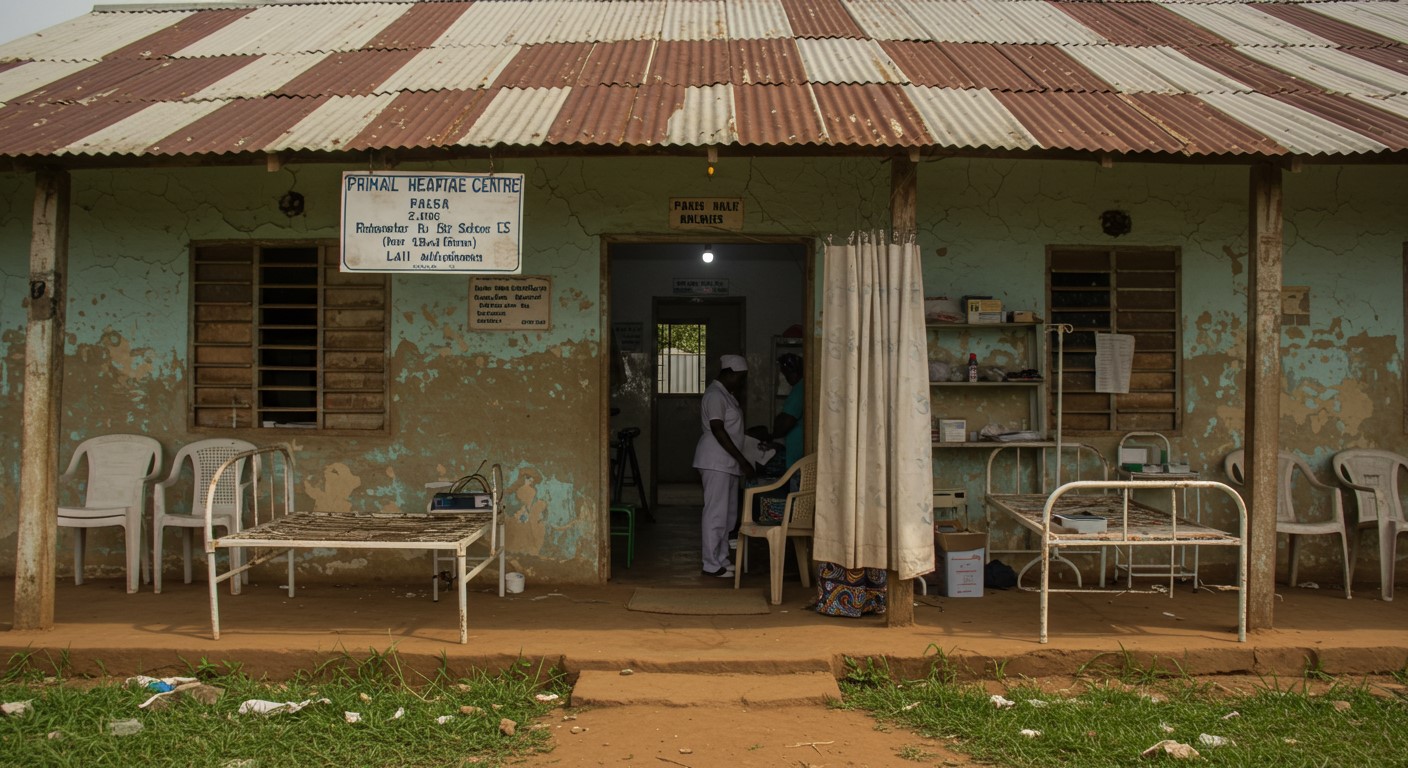
As we continue to tackle these issues from the grassroot level, we can also begin to envision what our primary health centers in Nigeria could become with the integration of technology. After all, seeing is believing. So here:
10 Ways Technology Can Transform Primary Healthcare in Underserved Regions
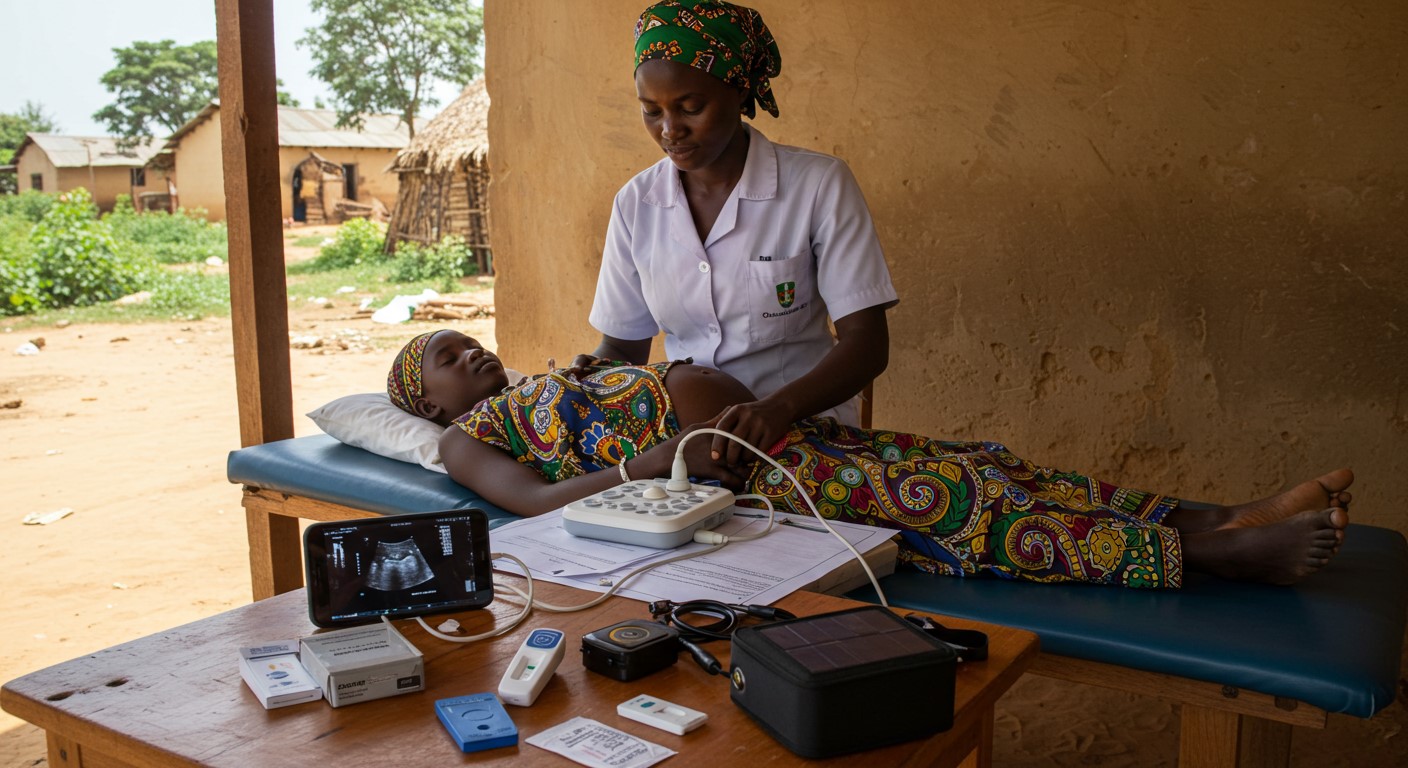
1. Portable Diagnostic Tools at the Frontline
Instead of waiting for lab results from distant hospitals, frontline health workers could use simple, low-cost diagnostic devices powered by mobile apps or solar energy. Tools for rapid malaria or anemia tests, mobile ultrasound devices, and digital stethoscopes can detect conditions early, saving lives before complications arise.
2. Telemedicine: Connecting the Disconnected
Telemedicine platforms allow patients in remote areas to consult with doctors via mobile phones or tablets. This not only reduces travel costs but also ensures timely expert opinions, especially in emergencies or maternal health cases.
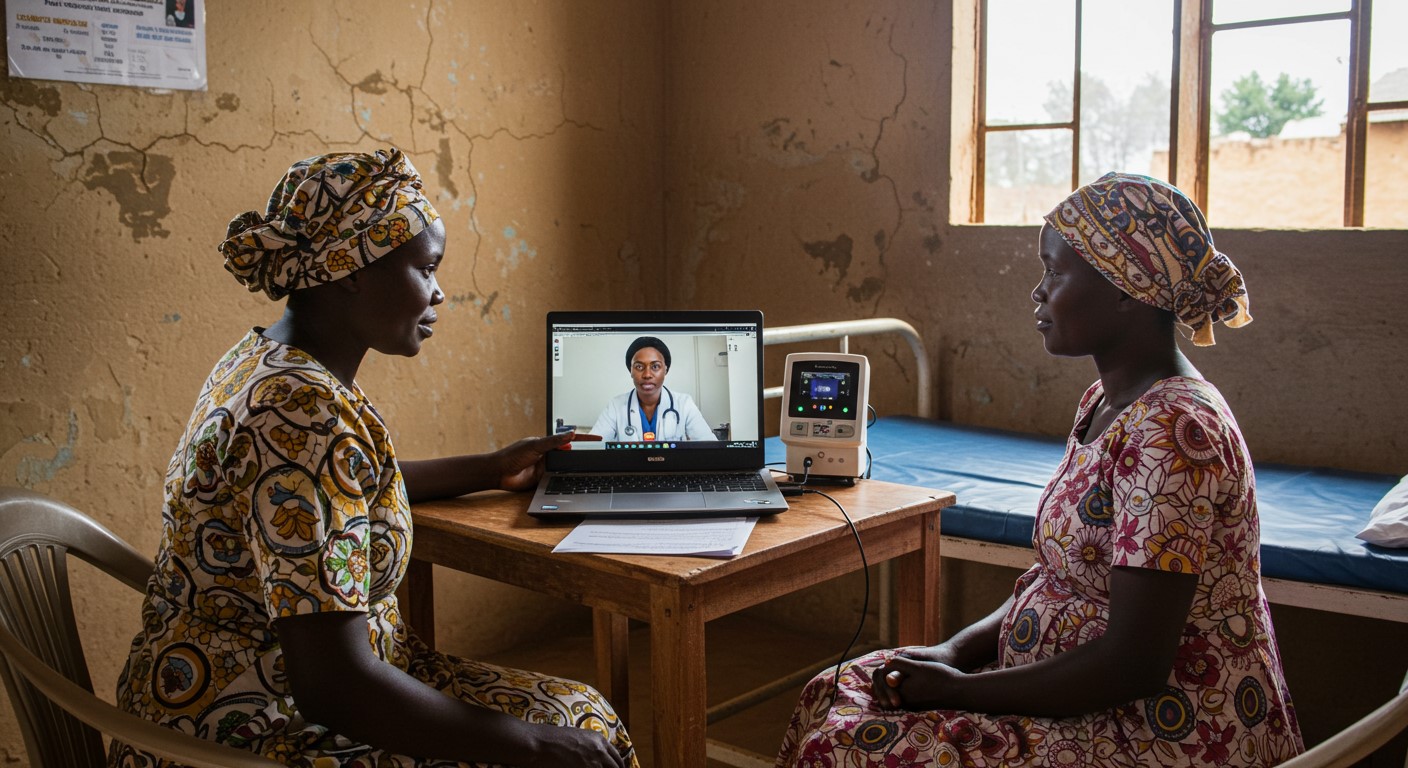

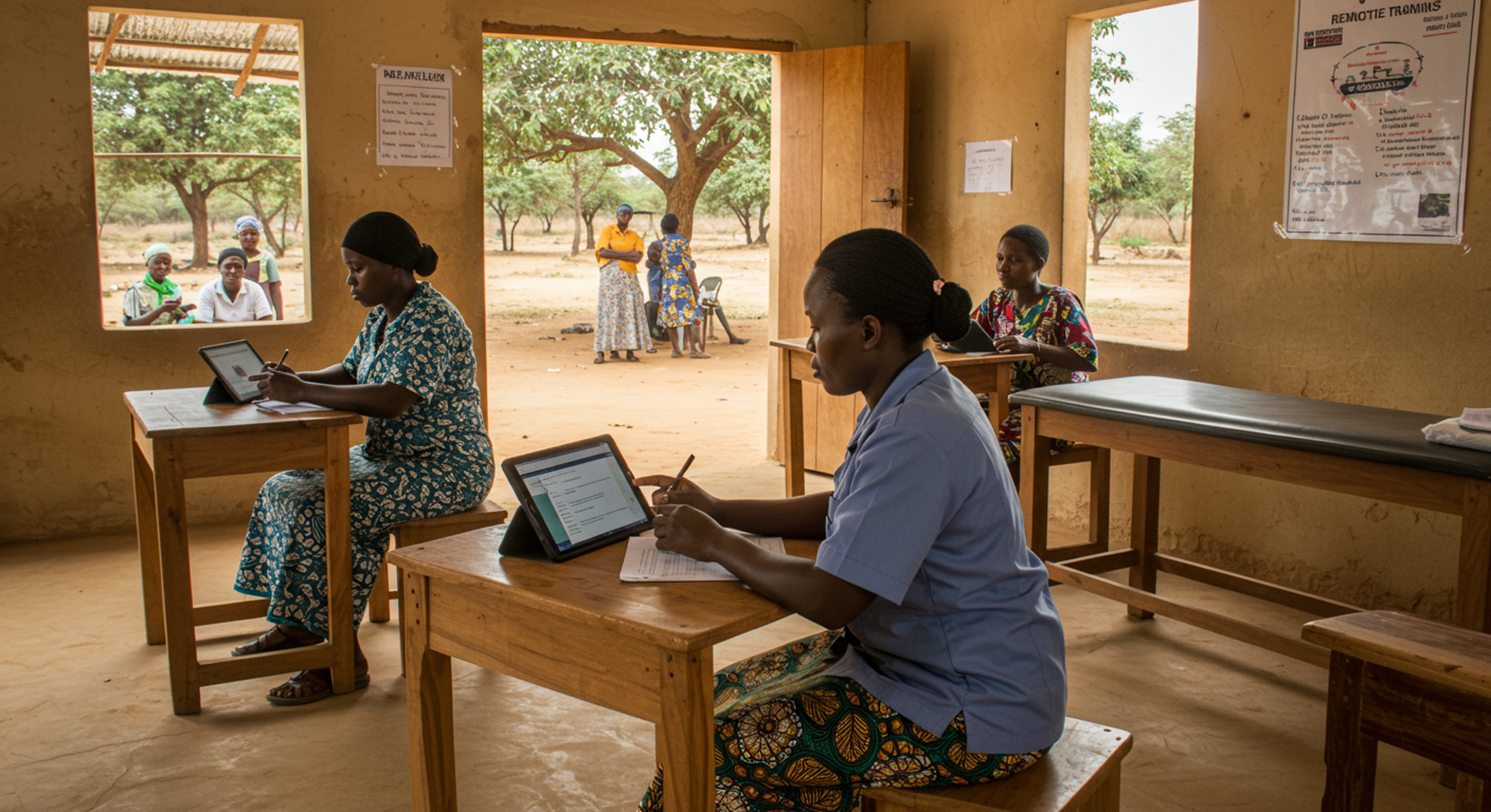
3. Data-Driven Health Decisions
Cloud based digital health records make it easier to track patient histories, vaccination schedules, and chronic conditions. Health workers can use tablets to update information on the go, enabling smarter decisions and follow-up care, even across different rural terrains.
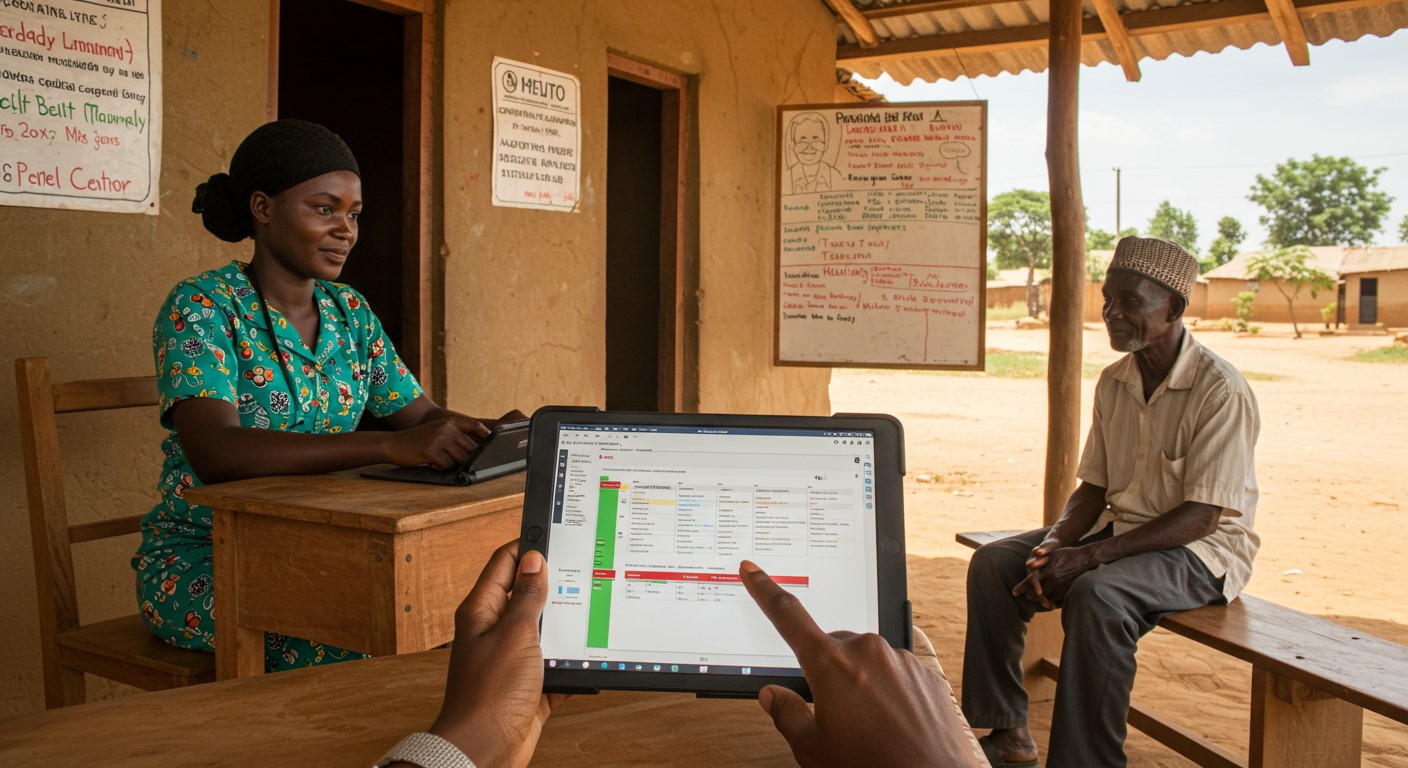

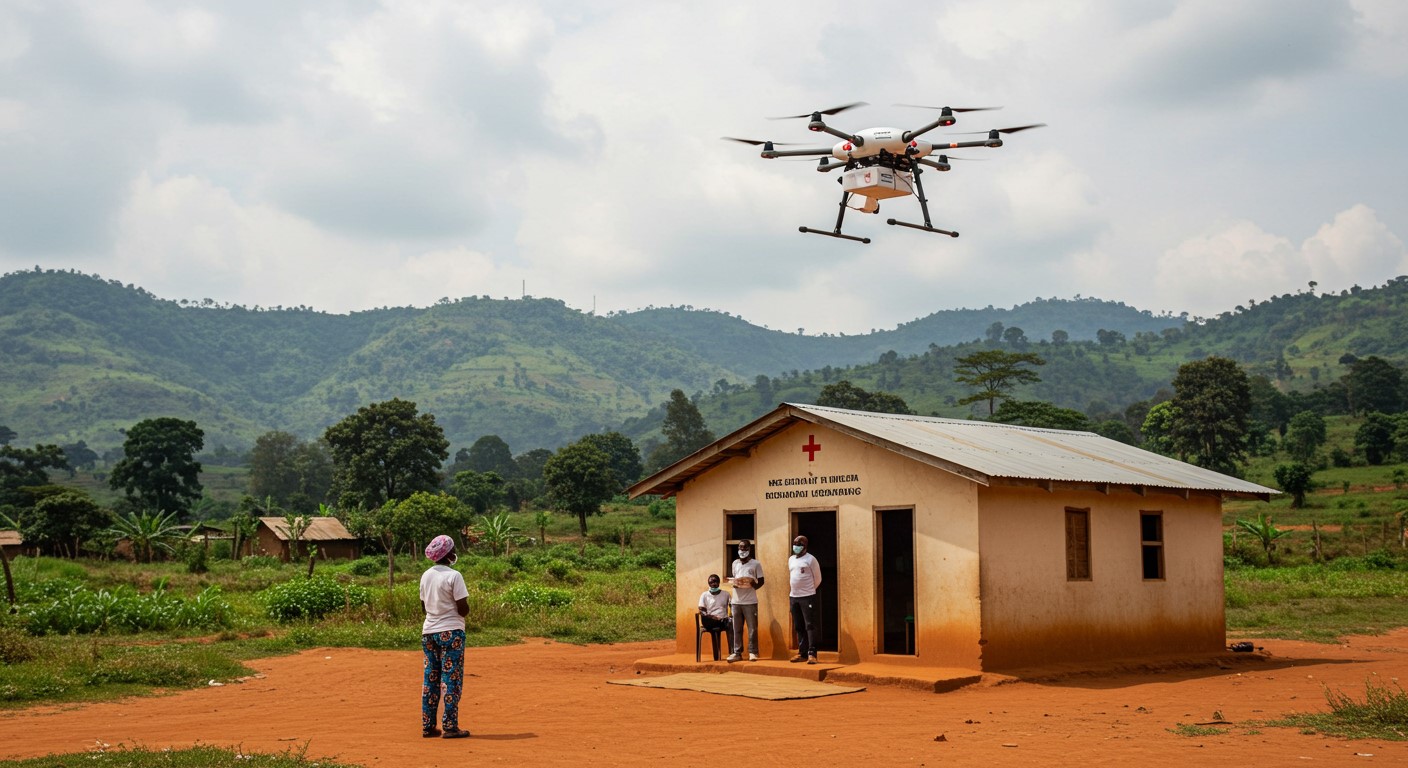
4. Emergency Medical Drones
In areas with poor road access, drones can deliver critical medical supplies like vaccines, blood, or antivenom in minutes. Rwanda and Ghana are already pioneering this solution with great success, and it could be adopted in other African countries with similar challenges.

5. Health Education via Mobile Apps
Technology shouldn't be for just healthcare providers, patients should benefit too from it. SMS alerts or mobile health apps can educate individuals and communities on topics like hygiene, nutrition, maternal care, disease prevention etc., in local languages, helping the people to take charge of their health.

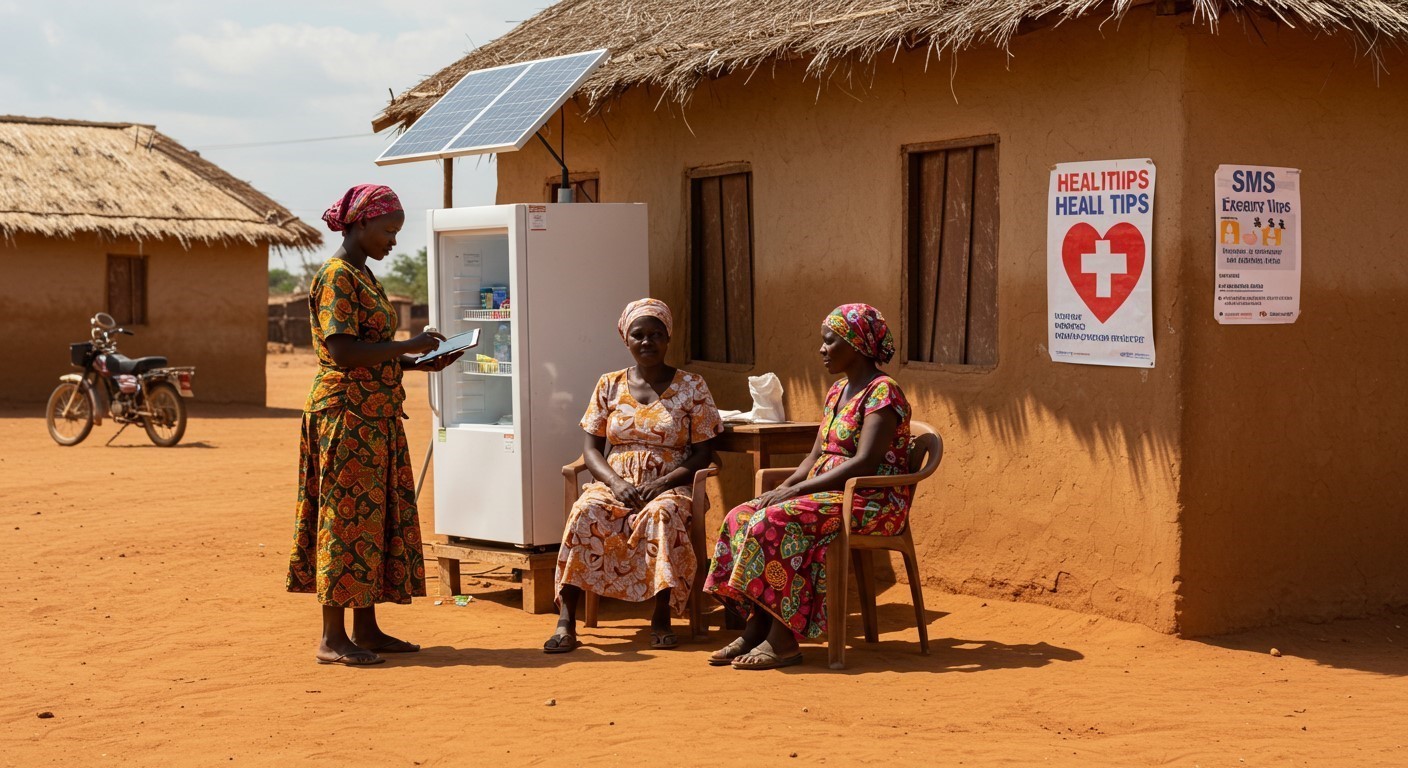
6.Solar-Powered Health Devices
Clinics without reliable electricity can still function using solar-powered fridges, devices, and lighting, especially for storing vaccines and running tests.

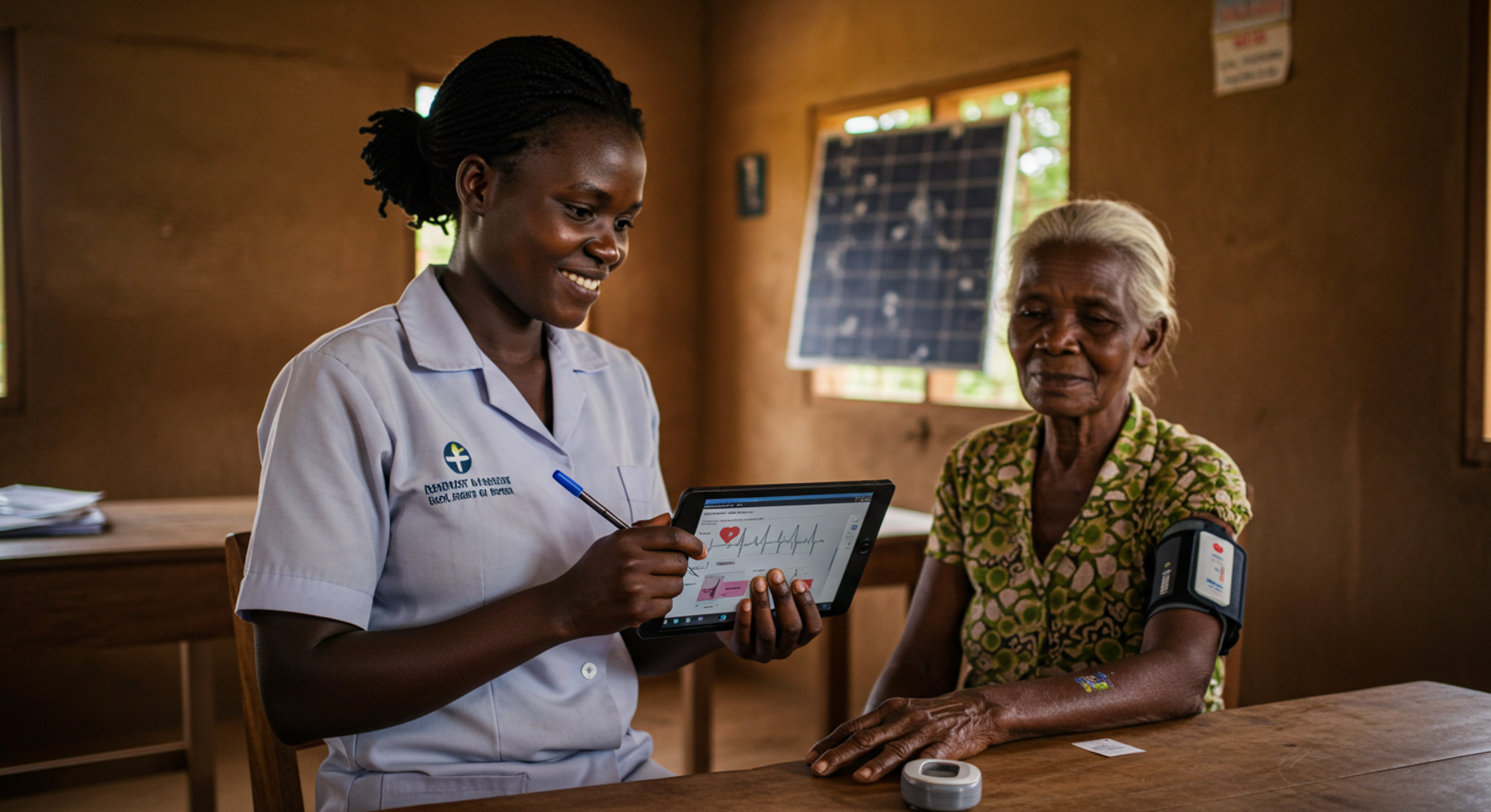
7.Wearable Health Monitoring Devices
Simple, low-cost wearables can help track vitals like heart rate, temperature, or blood pressure, allowing early detection of chronic or acute conditions.
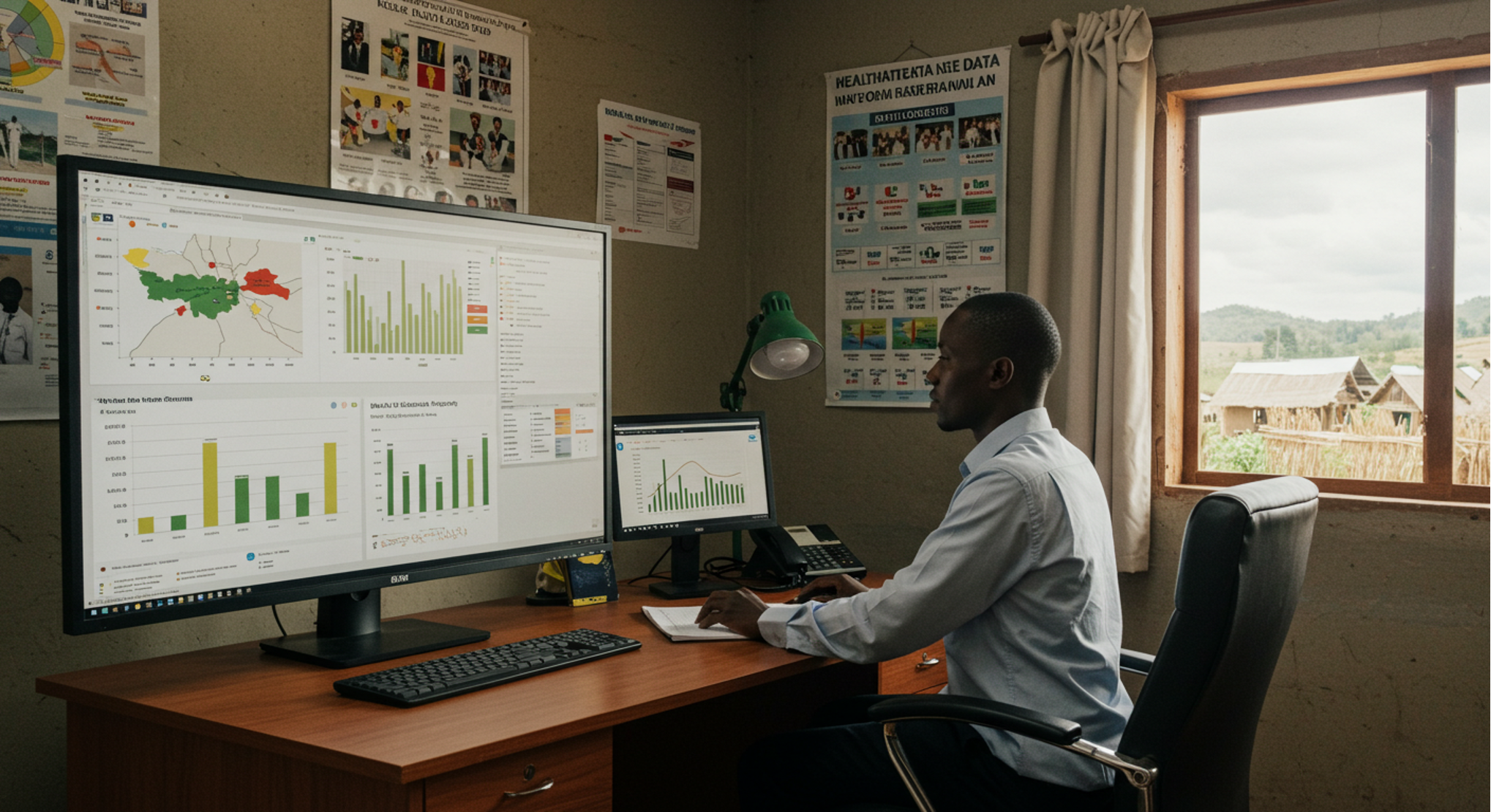
8.Health Data Dashboards for Policymakers
Aggregated data from communities can help government agencies and NGOs monitor outbreaks, allocate resources, and plan better interventions.
9.Remote Training for Community Health Workers
Health workers can receive advanced and most recent trainings and certifications through e-learning platforms, thus improving the quality of care they provide in the local communities they serve.

10.Remote Monitoring
Wearable devices that track vital signs such as, blood pressure, and glucose levels.

The Impact: Equity, Speed, and Better Health Outcomes
Tech-driven healthcare closes the gap for underserved populations by:
Reducing delays in treatment
Making services more consistent and affordable
Empowering local health workers with tools and knowledge
Increasing early detection and prevention rates
Food for Thought
As we return to our reality, it is important to acknowledge the challenges that come with adopting a technologically effective primary healthcare system in Nigeria. Despite these obstacles, we must continue to invest in innovations, funding, partnerships, and collaborations to turn these ideas into reality and this is because, every individual, regardless of where they live, deserve access to innovative, high-quality healthcare.

